Coupling
결합력
- 두 모듈의 상호의존성 정도
- 서로 영향을 덜 받는게 좋기 때문에 결합력은 낮은게 좋음
Low Couping System(결합력이 낮아진다면)
- 파동 효과 예방
- 이해성 상승
- why? 다른 모듈은 살펴볼 필요없이 해당 모듈만 확인하면 됨
Objective: Minimize coupling
- 가능한 독립적인 모듈들을 만들기
- 모듈이 잘 쪼개진 시스템
How to achieve low couppling(결합력을 낮추는 방법)
- 불필요한 관계 제거
- 필요한 관계의 수 줄이기
Scale of Coupling
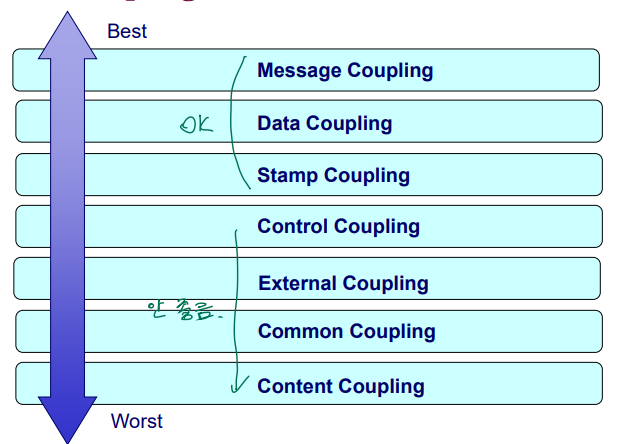
Message Coupling
- Message = 객체지향에서 메소드 호출(Public)
- 가장 느슨한 타입
- 객체(상태 분산으로 달성?)
- 파라미터 또는 메시지 전달같은 컴포넌트 커뮤니케이션
- 모듈은 서로 의존하지 않고 공개 인터페이스로 파라미터 없는 메시지를 교환
내부x, 인터페이스 정의로만 이어져있음
Data Coupling
- 파라미터 = 기본 데이터 타입(심플한 데이터 타입)
- 모듈들은 통신해야 함 => 데이터 커플링을 피할 수 없음 => 최소한 유지
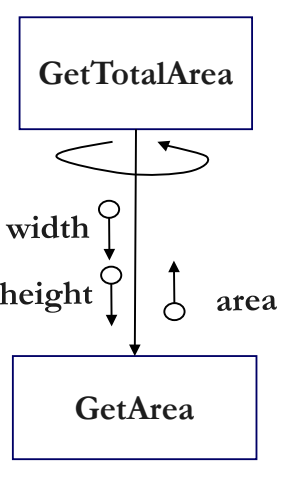
int GetTotalArea()
{
int totalArea = 0 ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ) {
totalArea += GetArea(shapes[i].width, shapes[i].height);//Data Coupling
}
return totalArea ;
}
Warnings on Data Coupling
넓은 인터페이스를 피해라
- 파라미터를 많이 쓰는 것
int ReadCustomerInfo(char* ID, char* name, char* address, char* phone, char* SSN)
{
}
int StoreCustomerInfo(char* ID, char* name, char* address, char* phone, char* SSN) {
}
해결: 구조체 사용
typedef struct _customerInfo {
char *name, *address, *phone, *SSN ;
} CUSTOMER_INFO ;
int ReadCustomerInfo(char* ID, CUSTOMER_INFO* info) {
}
int StoreCustomerInfo(char* ID, CUSTOMER_INFO info) {
}
TRAMP 데이터를 피해라
TRAMP 데이터
- 모듈이 원하지 않는 데이터
- 시스템 주변을 이동하는 정보 = 서플러 라운드
- 전달 목적에 의미가 없음 => 유지보수 관점에서 이해성이 떨어짐
- 많은 모듈을 통과할수록 실수로 변경되거나 결함이 확산될 가능성 높음
해결: 모듈 구조 재구조화
Stamp Coupling
- composite data(구조체)로 전달
- 데이터 구조에 모호성이 없어야함
- 너무 넓은 인터페이스는 피해야함
- 약간의 간접성 도입?
typedef struct _customerInfo {
char *name, *address, *phone, *SSN ;
} CUSTOMER_INFO ;
int ReadCustomerInfo(char* ID, CUSTOMER_INFO* info) {
}
int StoreCustomerInfo(char* ID, CUSTOMER_INFO info) {
}
Warnings on Stamp Coupling
문제1: 필요없는 정보 같이 전달 => 아마 TRAMP 데이터?
typedef struct _customerInfo {
char *name, *address, *phone, *SSN ;
} CUSTOMER_INFO ;
int ValidatePhoneNumber(CUSTOMER_INFO* info)//고객 정보 전달
{
/* 고객의 휴대폰 정보만 사용 */
}
- 연관없는 모듈 간 의존성 생성
- 모호성 상승
- 융통성 하락
- 불필요한 데이터 관여
해결1: 실제 사용되는 값만 전달
문제2: 번들링
- 연관없는 데이터들의 모음
- 쓸모없이 모호성만 상승
int CalcTototalPurchaseCost(int pricePerItem, int dicountType, int itemCount, int tax)// 개당 가격, 할인타입, 개수, 세금
{
}
typedef struct _stuff {
int pricePerItem, dicountType, itemCount, tax ;
} STUFF ;
int CalcTototalPurchaseCost(STUFF stuff) {
}
해결2-1: 연관없는 데이터를 모으지 마라
- 구조체 이름에 따라도 모호해짐
- 데이터 구조를 의미 있게 정의해야함
해결2-2: 간단한 데이터와 구조체 타입의 인터페이스 사용
Control Coupling
- 다른 모듈의 내부 로직을 제어하려는 의도로 전달
Forward Control
- caller가 callee의 행동 제어
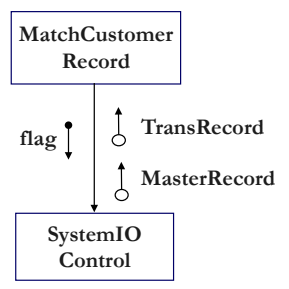
int GeneralIORoutine(int flag, void* buffer, int size) {
if ( flag == 0 )
/* READ data and store them into buffer */
else
/* WRITE data in buffer */
}
- 플래그 값에 따라서 행동을 결정 => 행동의 제한
- 로직 일부를 명시적으로 결정
- 의존적으로 동작
- 위처럼 결정하가 위해서 caller가 callee의 로직이 어떻게 구성되어있는 알아야함
해결: 불리는 모듈(Callee)을 분리
int Read(void* buffer, int size) {
/* read data and store them into buffer */
}
int Write(void* buffer, int size) {
/* write data in buffer */
}
- Caller가 내부 로직 결정 못함
Backward Control(=inversion of authority)
- 반대로 Callee가 Caller의 행동 제어

- Callee의 융통성이 줄음
해결: 서술적인 플래그 사용
| 유형 | 이름의 유형 | 예시 |
|---|---|---|
| Control flag (사용 => 상했다) |
동사 | 다음 레코드를 읽는다 (Read next record) 이 고객을 거절한다 (Reject this customer) 마스터 파일을 되감는다 (Rewind master file) |
| Descriptive flag | 형용사 | 달걀이 썩었다 (Egg is rotten) 우편번호가 숫자이다 (Zip code is numeric) 거래 파일이 끝에 있다 (Transaction file is at end) |
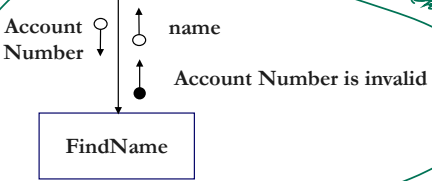
- 계좌번호가 유효하지않다는 메시지가 나음
External Coupling
- 외부에 존재하는 하나의 공통된 정보를 공유
- 외부 파일
- 디바이스 인터페이스(=Standard I/O)
- 프로토콜
- 데이터 포맷
- 외부 도구와 기기와의 통신과 관련
Common Coupling
- 같은 전역 변수 영역 관여
안좋은 이유
- 파동효과
- 적은 유연성
- 시간의 원격성(=정보전달의 의도를 가진 공유 변수 사용의 시차)?
- 다중 목적으로 전역 변수 오용
- 이전에는 a로 쓰고 이후에는 b로 써서 목적이 혼돈
- 전역 변수 사용을 트랙킹하고 이해하는게 어려움
해결: 전역변수를 의미있는 파라미터로 변환
- 정확, 이해성 상승
- 변수에 대한 수정이 다른 모듈의 영향을 줄임
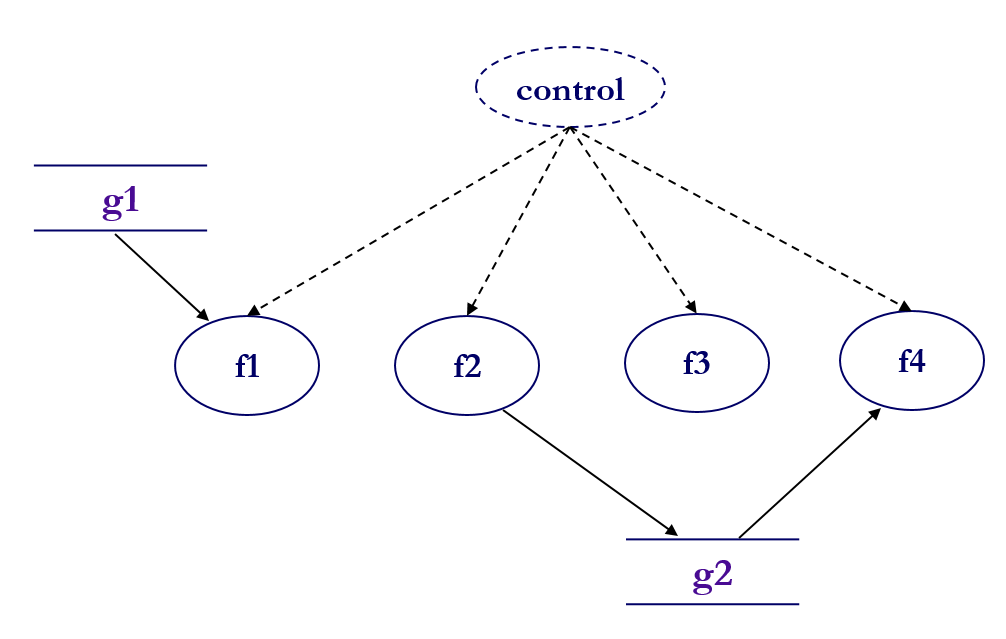
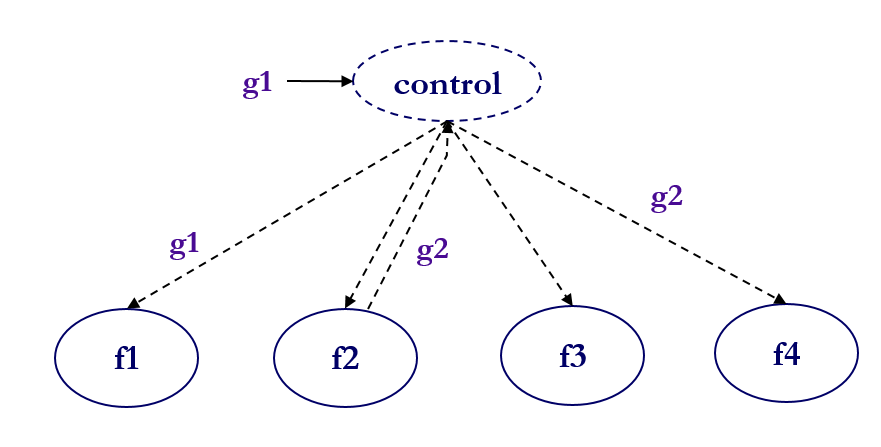
해결: 전역 변수 선언을 제한하고 지역 변수(scoped variables) 사용
int gA, gB, gC, gD, gE ;
void f1( ) {
/* access gA, gB, gC */
}
void f2( ) {
/* access gA, gB, gC */
}
void f3( ) {
/* access gD, gE */
}
void f4( ) {
/* access gD, gE */
}
위 코드를 아래와 같이
static int gA, gB, gC ;
void f1( ) {
/* access gA, gB, gC */
}
void f2( ) {
/* access gA, gB, gC */
}
static int gD, gE ;
void f3( ) {
/* access gD, gE */
}
void f4( ) {
/* access gD, gE */
}
해결: 전역 변수에 대한 접근 함수 정의
- ex) get, set
- 직접적으로 전역 변수에 접근X
/* A.c */
static int gA;
void setA(int a) {
gA = a ;
}
int getA( ) {
return a ;
}
/* B.c */
static int gB;
void setB(int b) {
gB = b ;
}
int getB( ) {
return b ;
}
void f1( ) {
int x = getA( ) ;
setA(x++) ;
}
void f2( ) {
int y = getB( ) ;
setB(y+getA( )) ;
}
void f3( ) {
int z = getD( ) ;
setE(z+getE( )) ;
}
void f4( ) {
int u = getD( ) + getE( ) ;
setE(u) ;
}
Content Coupling
- Content(내용)에 내부라는 의미 포함
두 모듈이 내용 결합(Content Coupling) 상태에 있다면, 한 모듈이 다른 모듈의 내부를 참조하거나 변경하는 방식으로 연결된 것을 의미합니다. 아래는 이에 대한 요약입니다:
-
모듈이 다른 모듈 내부를 참조하거나 변경할 때:
- 한 모듈이 다른 모듈의 데이터를 직접 접근하거나 변경하는 경우.
- 예: 한 모듈이 다른 모듈 내부의 변수나 상태를 직접 수정함.
-
모듈 간의 흐름 제어:
- 한 모듈이 다른 모듈의 분기(branch)나 흐름(fall-through)에 영향을 미치는 경우.
-
예시:
- 어셈블리 프로그램에서 모듈 간의 직접적인 접근.
goto와 같은 명령문을 사용해 한 모듈이 다른 모듈로 직접 이동.
문제점: 내용 결합은 모듈 간의 높은 의존성을 초래하여, 유지보수와 확장성을 어렵게 만듭니다.